There’s so much to discuss when it comes to cannabis extract. From the products themselves to the preferred methodology used to create them and new medicinal uses, there’s a lot to unpack. General knowledge and understanding of what cannabis extracts are, how they differ from other cannabis products, and what consumers expect when purchasing them is a great place to start.
Cannabis Extract Basics
Cannabis extract falls under the category of cannabis concentrates. Extracts are created using solvents to separate the cannabinoids and terpenes from the cannabis plant. Solvents used for this separation can include butane, propane, ethanol, or supercritical carbon dioxide (CO2). Alternative solventless extraction methods exist as well, but we will primarily focus on cannabis extracts produced with solvent-based extraction for this article.
One of the great allures of cannabis extracts is providing alternatives for cannabis consumers at both ends of the market spectrum. For example, individuals who are averse to the potential smells, tastes, or euphoric highs of smoking flower can consume cannabis extracts instead. For experienced consumers who want to amplify the flower’s flavors and receive a more intense and “fuller” euphoria, several other extracts fit the bill. The range of consumer needs fulfilled with extract products continues to propel the popularity of cannabis extracts, especially in recreationally legal states.
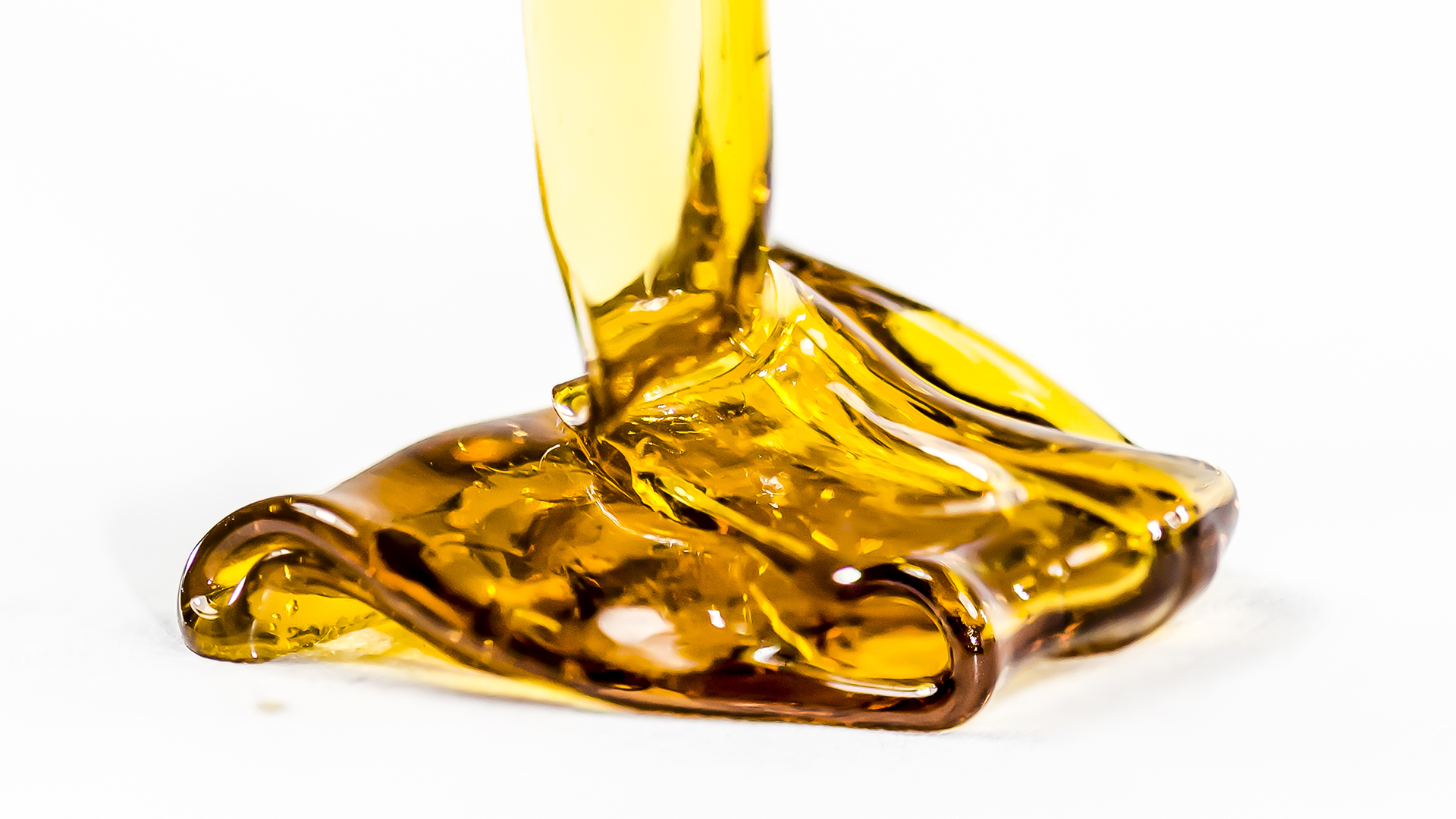
Additionally, extracts are considerably more refined, making for a cleaner product with fewer unnecessary substances. Cannabis extracts vary in texture, elemental state, and processing.
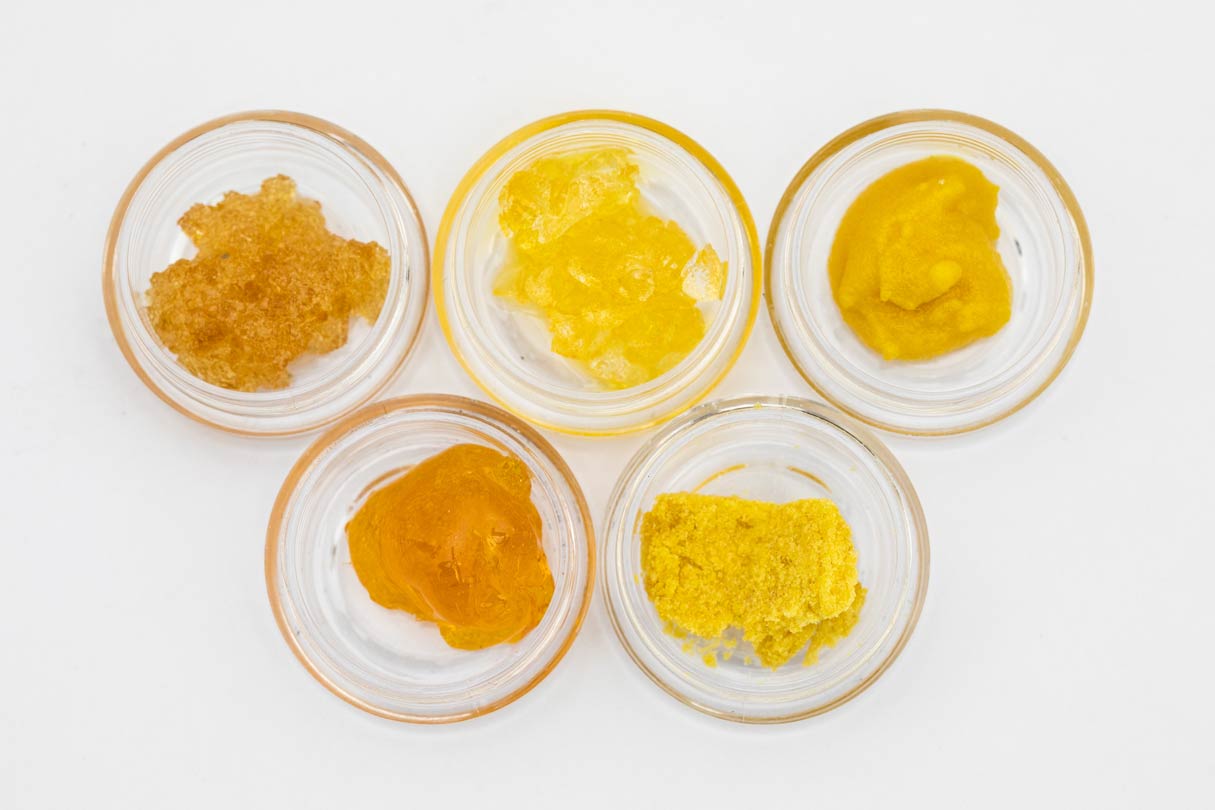
Types of Cannabis Extracts

Crude Oil
Solvent Used: Hydrocarbon Consumption Method: NA Crude oil is the extract collected at the conclusion of the primary extraction run when dried, or cured flower has been used. This extract is not consumed but further refined in post-processing steps to make a consumer product.

Live Resin
Solvent Used: Hydrocarbon Consumption Method: NA Live resin is also an extract collected at the conclusion of the primary extraction run. However, in this instance, fresh plant that has been frozen is used as the source material instead of dried flower.

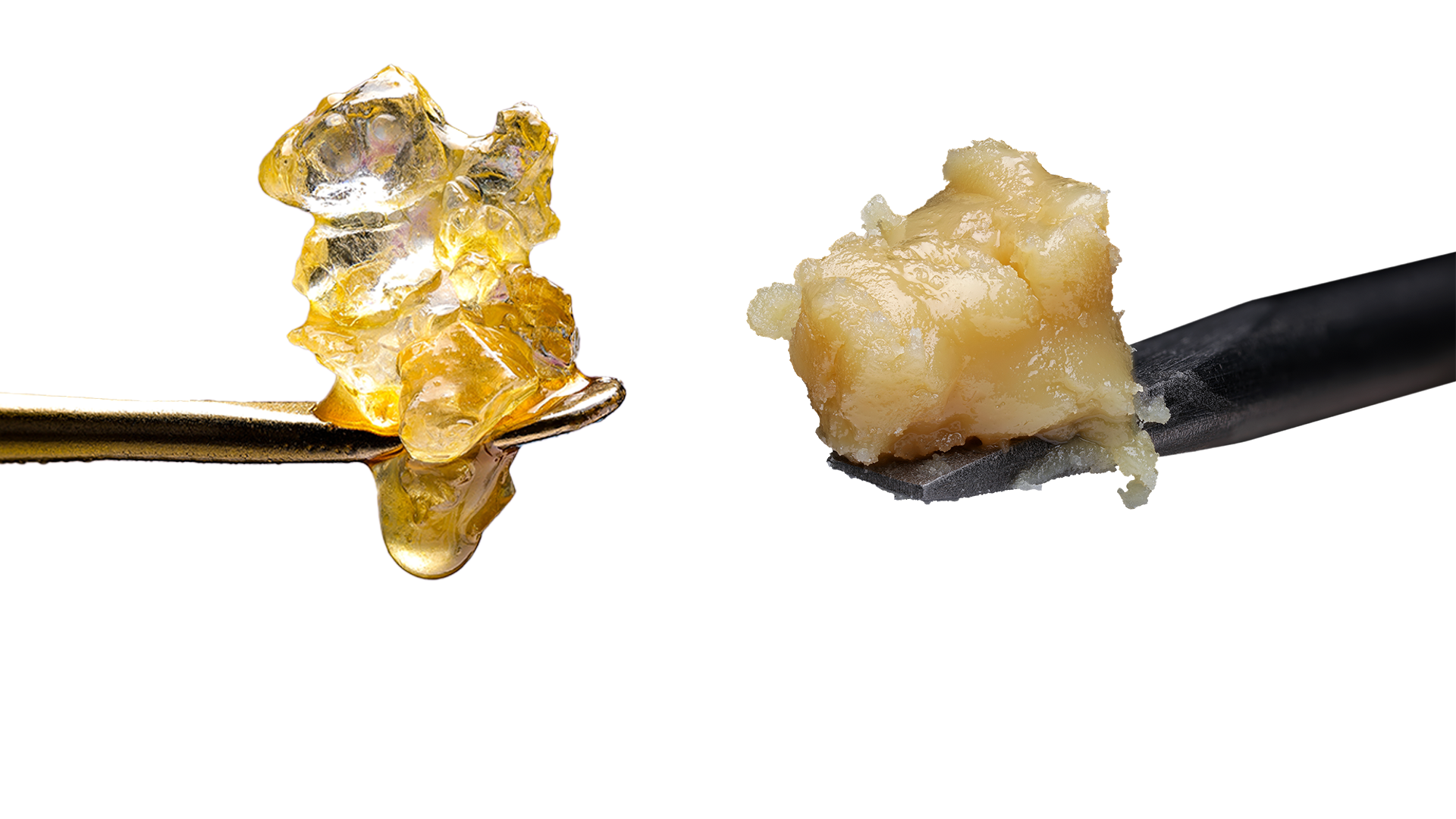
Shatter
Solvent Used: Hydrocarbon Consumption Method: Dabbing Shatter is a product made from dried or cured flower. This product is a hardened and glass-like consistency, and like its name, will shatter. It looks like a thin, golden-colored sheet.

Badder
Solvent Used: Hydrocarbon Consumption Method: Dabbing Badder, or butter, is also made from live resin or cured resin extract; see definition above. It has a cake batter consistency achieved by “whipping” and contains a moderate amount of terpenes.

Sugar
Solvent Used: Hydrocarbon Consumption Method: Dabbing Sugar is also a product made from live resin extract. However, many concentrate manufacturer’s often name and advertise “sugar” as “live resin” on the dispensary shelves. This extract has a sugary, grainy-looking appearance and is essentially wax with crystals in it.

Wax
Solvent Used: Hydrocarbon Consumption Method: Dabbing Wax is a concentrate made from live resin or cured resin extract and has, as the same suggests, a waxy consistency. The color tends to be a bit lighter, more opaque than something like shatter or sugar. The wax-like consistency is achieved through heat and agitation.

Sauce
Solvent Used: Hydrocarbon Consumption Method: Dabbing Sauce is another product made starting with live resin cannabis extract. It contains a mixture of THCa crystals (see THCa Crystalline definition below) and is mixed with isolated terpenes, giving it a soupy appearance.

THCa Crystalline
Solvent Used: Hydrocarbon Consumption Method: Oil, pill, drink (for non-psychoactive effects), or dabbing (for psychoactive effects) THCa Crystalline is a highly refined crude oil cannabis extract with the physical appearance of crystals. It has a potency of ~99.96% THCa and is considered an “isolate” because it lacks the other terpenes and cannabinoids found in the originating crude oil. Depending on the method of consumption used (i.e., heat or no heat), the user will either feel an intense psychoactive effect or no euphoric high at all.

THC Distillate
Solvent Used: Ethanol (most common) or Hydrocarbon Consumption Method: Food, drink, pills, tinctures, vape cartridges THC distillate is a distilled form of crude oil. Using fractional distillation, the cannabinoids are isolated from the other compounds in the oil to create a flavorless, odorless concentrate that can be further processed or refined into various consumer products.

Full Spectrum CBD
Solvent Used: Ethanol (most common) or Hydrocarbon Consumption Method: Food, drink, lotion, pills, oils Full-spectrum CBD extract is made from crude oil and contains a full spectrum of cannabinoids and terpenes from the cannabis plant. Hemp is traditionally used for making full-spectrum CBD extract rather than marijuana. This CBD extract can contain low THC levels, below 0.3%, or marketed as “THC-free” with THC levels below 0.1%.

CBD Distillate
Solvent Used: Ethanol (most common) or Hydrocarbon Consumption Method: Food, drink, vape cartridges CBD distillate is a purified and distilled form of hemp crude oil using fractional distillation. It has an oil-like consistency that is odorless and flavorless. It can be further processed into a variety of other consumer products. Distillate is not considered a full spectrum extract because of the removal of other cannabinoids during the distillation process.

CBD Isolate
Solvent Used: Ethanol (most common) or Hydrocarbon Consumption Method: Lotions, edibles, drinks, pills, dabbing CBD isolate is a further refined CBD distillate. After fractional distillation, the oil is subjected to additional solvent, temperature changes, and motion resulting in a crystal-like structure. Often these crystals are ground down to a powder-like consistency and used in an end product. This cannabis extract is free of other cannabinoids and terpenes and is 99% pure CBD.
How Does Cannabis Extract Processing Work
Cannabis extraction uses a hydrocarbon or ethanol solvent to separate THC, CBD, and cannabinoids from the cannabis plant matter, which leaves an oil-like extract. A complex, multi-step process, when it’s consistently performed correctly, it yields refined products.
The initial step in the cannabis extraction process is separating the cannabinoids and terpenes from the unwanted plant matter using a solvent best suited for the end product in mind. This phase is referred to as primary extraction.
The next few steps to follow in purifying or refining the cannabis extract can include color remediation, winterization, filtration, and terpene removal. These are then followed by decarboxylation, distillation, and potentially crystallization. These steps in cannabis extract development play a pivotal role in the isolation, refinement, and purification of the desired components to create a fine-tuned product.
An essential item to note in this guide to cannabis extract is that the team behind the complex process is paramount. One of the critical mistakes made by cannabis extraction businesses is the failure to assemble a high-quality, knowledgeable team of scientists, chemists, and experienced support personnel.
Equipment For Making Cannabis Extracts
Precision is a leading provider of extraction and post-processing equipment for cannabis and hemp. no matter what cannabis extract you’re trying to make, we can help you get there. Equipment systems are available from primary extraction through to final post processing, including ancillary equipment needs. Are you ready to find the optimal system for your operational goals? Talk to an extraction expert today!