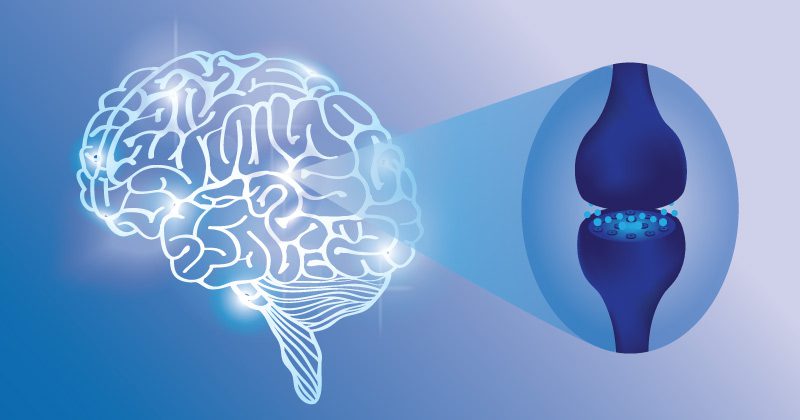
Whether a consumer enjoys cannabis products for medicinal or recreational purposes, the desired effects would be impossible without the human body’s endocannabinoid system.
Despite its biological significance in the way humans consume and experience the effects of cannabis, the endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a relatively recent scientific discovery. So current, in fact, that to this day, experts still have lingering questions about the system’s function within the body.
Put simply; the endocannabinoid system is the system that regulates many biological functions that enable us to feel the desired effects of cannabis products. It is what allows our bodies to interact with chemicals like those found in cannabis products.
The internal system’s makeup consists of three parts, including cannabinoid receptors, endocannabinoids, and enzymes. Each plays its unique role in its functionality. The endocannabinoid system helps regulate essential human functions like sleep, appetite, pain, and more, through endocannabinoids that the body creates naturally. It also interacts with cannabis and enables CBD and THC products to benefit those same human functions.
Endocannabinoid System Specifics
The ECS functions as a neuromodulatory system. This means that it serves the body for interpreting our surroundings and dealing with environmental factors like impending risk, potential reward, and more. Following these signals, neuromodulatory systems help enable our cognitive responses like emotional reactions and decision-making. It plays a specific role in our human instincts and survival, and the critical regulation of particular functions necessary to survival.
The Importance of Homeostasis
The science behind the endocannabinoid system is challenging to comprehend without an understanding of homeostasis. Homeostasis is a biological concept that neuromodulatory and like systems function to maintain optimal conditions for human performance and comfort. An example of this is body temperature. When your body is working at optimal levels, you’re neither uncomfortably hot nor extremely cold. This optimal state is called homeostasis.
The ECS plays a significant role in the body’s ability to maintain homeostasis because of its impact on essential human biological functions like sleep, appetite, pain, and more.
The Biological Structure of the Endocannabinoid System
The endocannabinoid system has locations throughout the human body. From fingertips to toes to the brain, it exists almost everywhere as a tool to regulate homeostasis. The three critical pieces of the system (the receptors, endocannabinoids, and enzymes) act as an assembly line of sorts to gather signals, influence signals, interpret signals, and act.
An example of this function is easily explained with pain sensations. Imagine a minor bone fracture. These fractures result in damage to several types of cells, and the area creates the resulting warning of extreme pain. Heightened blood flows into the affected area to begin the healing process. Once the patient gets the bone set, and this pain and healing response is no longer necessary, the body will regulate itself back to normal functions. This process is triggered, works effectively, and resolves because of the endocannabinoid system.
Endocannabinoid Receptors
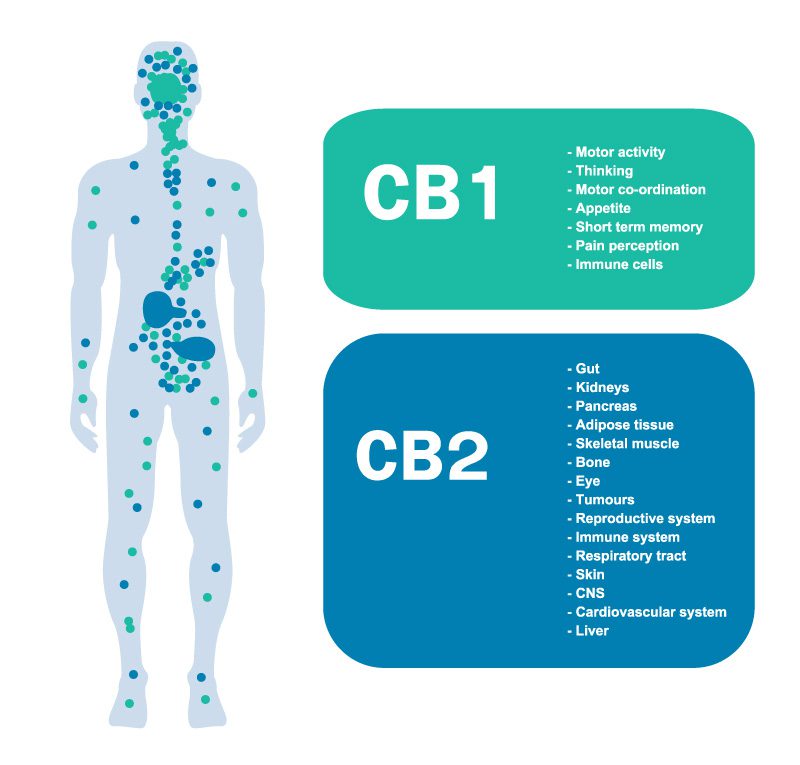
When endocannabinoids bind to endocannabinoid receptors, it signals the ECS to take action. The two main types of endocannabinoid receptors that are found in the human body are:
CB1 Receptors: These are primarily found in the central nervous system and are very abundant in the brain and spinal cord. Some endocannabinoids target CB1 receptors in spinal nerves to help relieve pain.
CB2 Receptors: These are found in the peripheral nervous system, most often in immune cells. Specific endocannabinoids bind to a CB2 receptor in the immune cells to signal to the body that tissues are experiencing inflammation, which is a sign of autoimmune disorders.
Endocannabinoids can bind to either receptor. The effects of cannabis directly correlate to the signals of the endocannabinoid system because of their interaction with the CB1 and CB2 receptors. CB1 responders are responsible for the psychoactive effects of marijuana, while CB2 receptors are currently a popular research topic for scientists studying ways to fight inflammation and cancer.
The Endocannabinoid System and Cannabis Products
As any avid cannabis consumer knows, each CBD and THC product holds different types of benefits. For example, CBD oil reduces pain and inflammation, provides anxiety relief, and can be used to develop a healthier lifestyle. An array of cannabis extracts and concentrates are being produced to allow users to better tailor their desired experience and need for cannabinoids in their day to day lives.
Ultimately, understanding how our body responds to cannabis products enables us to better appreciate the medicinal and recreational value of marijuana and hemp plants.

Teach Me More: The Ultimate Cannabis Extract Guide
Now that we know what the endocannabinoid system is and how our body reacts to cannabinoids, let’s explore what cannabis extracts are, how they differ from other products containing cannabinoids, and what consumers should expect when purchasing them.